
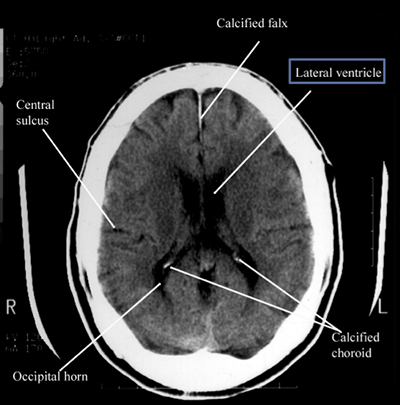
Tumor bed, cranial nerve, and elective target volumes are depicted.
We provided detailed contouring and planning guidelines on a CT atlas, with figures to help illustrate internerve connections, based on clinical experience, literature-based patterns of failure, and established anatomic connections between cranial nerves. All of the images were then reviewed with a diagnostic radiologist to establish consensus for delineating the cranial nerves. The cranial nerves V2, V3, VII, and XII, and sample primary tumor sites were initially delineated using the Varian Eclipse planning system by 5 radiation oncologists. Representative patient diagnostic computed tomographic (CT) scans with contrast of the neck were used to create example contours. This contouring guide attempts to address this need. Atrioventricular heart valves, that is, the mitral valve and the tricuspid valve, play vital roles in our cardiovascular system.

#Qarc ventricles altas how to
When adjuvant radiation to cranial nerves at risk in head and neck cancers with PNI is considered, there is a need for consensus on which nerves are at risk and how to contour these nerves. aortic stenosis: less common with a QAVĪ first description of a quadricuspid aortic valve was thought have been described by Balingen in 1862 8.Perineural invasion (PNI) is a frequent pathological finding in head and neck cancers.aortic incompetence/ aortic regurgitation: considered most common hemodynamic abnormality associated with a QAV and is hypothesized to be the result of progressive valve leaflet thickening and asymmetric mechanical stress causing abnormal leaflet coaptation (some studies report aortic regurgitation to be present in up to 75% of people with a QAV at the time of diagnosis 8).MRI also has the advantage of demonstrating the dephasing jet corresponding to regurgitation associated with QAV. The morphology of the valve anomaly can be evaluated using cardiac MRI. Short-axis views of the aortic valve on echocardiography show the characteristic appearance of a QAV: an X configuration during diastole and a square configuration during systole MDCT - Cardiac CTĬT not only can depict the morphology of the valves, but also can provide information on the presence of stenosis and regurgitation using retrospective ECG gating, which allows data to be reconstructed in multiple phases of the cardiac cycle and the images can be viewed in cine mode. Has been the traditional method of diagnosis.

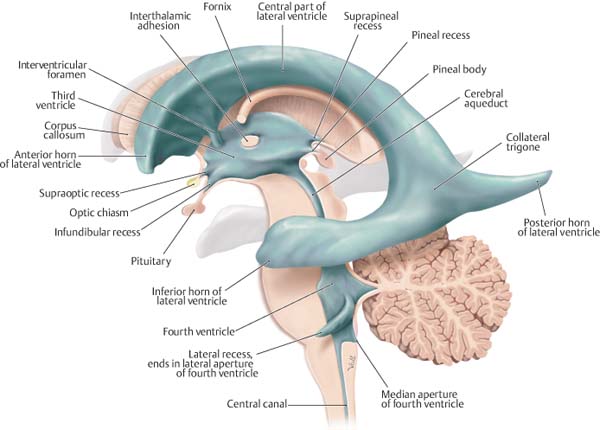
type f: two equal-sized large cusps and two smaller cusps not equal in size.The cortex was parcellated into 43 regions (Online Supplemental Data) in each cerebral hemisphere for a total of 86 regions. type e: three equal-sized cusps and one larger cusp The ventricle atlas included the lateral and third ventricles.type d: one large, two indeterminate and one smaller cusp.type c: two equal sized large and two equal smaller cusps.type b: three equal-sized cusps and one smaller cusp, considered commonest variation 1.IROC Rhode Island (QARC) is part of the Imaging and Radiation Oncology Core Group (IROC), a member of the NCI National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN). We are a research program within the Department of Radiation Oncology at the UMass Chan Medical School. The method that was traditionally described by Hurwitz and Roberts includes 5: Welcome to the IROC Rhode Island (QARC) website. single orifice for the coronary arteries or presence of an accessory artery) and displacement of the coronary ostia because of the accessory cusp congenital coronary artery anomalies (e.g.These ventricles have three horns projecting into the lobes for which they are named. It’s designed to operate dual-mode sound locomotives that include the latest QSI Quantum Analog Remote Control (QARC) system. AssociationsĪ quadricuspid aortic valve is usually isolated but can be occasionally associated with other cardiac anomalies, such as: There are two C-shaped cavities called the lateral ventricles one in each cerebral hemisphere. Some reports suggest that this anomaly may be in up to 1% of individuals who present for aortic valve surgery 6. There is no recognized gender predilection. While the incidence of QAV on 2D echocardiography has been reported to range between 0.01-0.04%. The estimated incidence on necropsy at ~1 in 8,000.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
